Researchers demonstrate the importance of smart networks for efficient water management
A comprehensive review study, authored by researchers from VŠB-TUO and Mendel University in Brno and published in the prestigious journal ACM Computing Surveys, delineates current advancements in integrating Internet of Things (IoT) and artificial intelligence (AI) for efficient and sustainable water management. The publication offers an in-depth analysis of the state-of-the-art and defines primary future research challenges.
The processes of water treatment, monitoring, and distribution constitute critical components of national infrastructure, with escalating demands on water distribution networks (WDNs). Water resource managers are confronted with challenges such as increased surface and groundwater extraction driven by climate change and droughts, as well as substantial water losses during transmission to end-users. The implementation of IoT systems and intelligent distribution networks presents a promising solution for enhancing operational efficiency and safety, as well as for facilitating leak detection in the event of a failure or unauthorized consumption.
“This type of smart network, referred to as Smart Water-IoT (SW-IoT), is a new, comprehensive concept for water management. In our review study, we looked at the application of IoT and artificial intelligence components in five key areas: agriculture, water treatment, safety, water supply networks, and wastewater treatment. The study also provides an overview of relevant legislation in the EU, US, Canada, Australia, China, Japan, and India. In this context, it also outlines the mandatory implementation of smart solutions for remote data reading in the critical infrastructure of EU member states, which highlights the importance of responsible water management,” said one of the authors of the article, Radek Martinek from the Faculty of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science at VŠB-TUO and the Industry 4.0 & Automotive Lab of the REFRESH project.
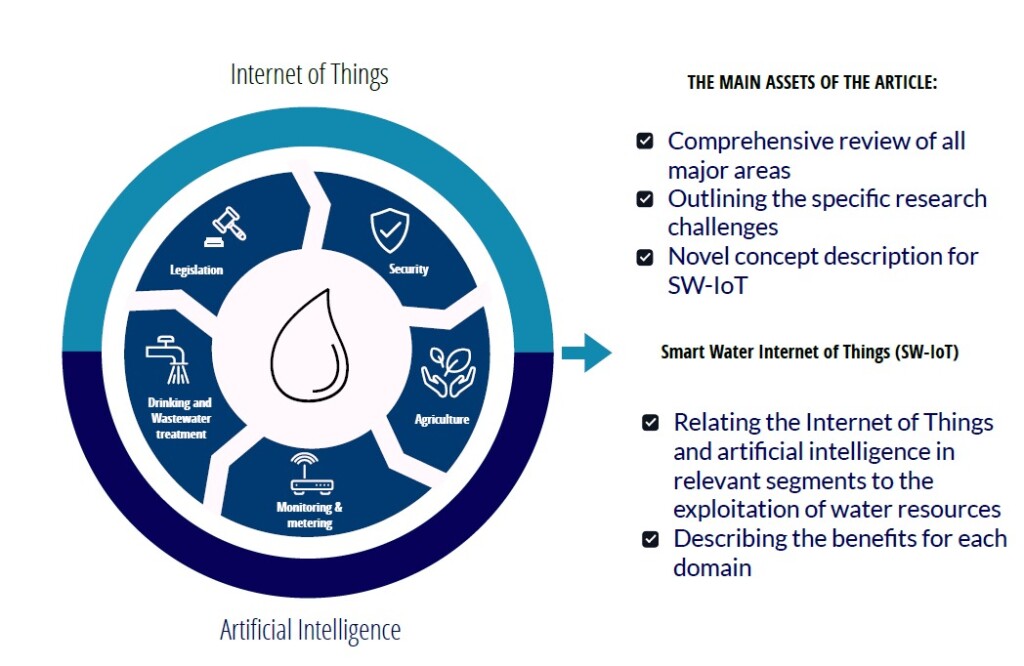
The authors focused not only on the possibilities of developing technologies that contribute, for example, to the optimization of water treatment processes and energy efficiency, but also on their safety and economic use. “Smart technologies utilized to monitor and control these processes also carry risks and can be misused for illegal purposes. It is therefore necessary to develop cybersecurity and early warning systems to protect this critical infrastructure. In agriculture, research should focus on increasing irrigation efficiency and water conservation so that water resources are used as efficiently as possible. Smart technologies can be employed, for example, to accurately predict the weather, which helps with effective water management,” said Martinek.
The authors advocate for the development of comprehensive legal frameworks to regulate the deployment of smart water management systems, alongside the adoption of advanced AI methodologies for data processing and storage. The main objective should be to protect this data from unauthorized access and misuse. Furthermore, the authors underscore the importance of establishing liability mechanisms pertaining to health or property damages resulting from failures of these intelligent systems.